What do you mean by mutual funds:-
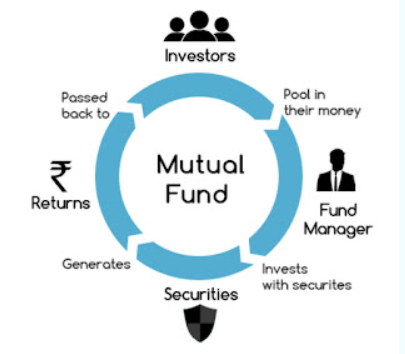
A mutual fund is a pool of money that is managed by a professional fund manager. It is a trust that pools money from a large number of investors who shares a common investment objective and invests the same in equities, bonds, money market instruments or other securities.
Mutual fund is a process of pooling resources from the investors and investing funds in securities. The process of pooling the resources together and. issuing units to the investors and then investing funds in securities is known as the scheme of “Mutual Funds”.
In other words, it works like a trust which pools the savings of investors and invests these in capital and money market instruments. Mutual funds offer good investment opportunities to the investors. Like all investments, they also carry certain risks.
Different Types of Mutual Funds :-
Mutual funds are broadly classified into four different types based on the asset class in which they invest – Equity Funds, Fixed Income Funds, Money Market Funds and Hybrid Funds. The mutual funds types briefly description are as follows :-
1.EQUITY FUNDS :-
As the name suggests, Equity Funds are a type of mutual funds that primarily invest in shares of various companies. Since these funds invest in the equity market, they carry a high degree of investment risk. That said, the potential for capital appreciation is also high with these types of mutual funds.
While the general theme of equity funds is the same, not all of them are similar or comparable to each other. While some equity funds may choose to invest in just one or several sectors, others may try to mirror an index such as the Nifty 50.
2.FIXED INCOME FUNDS :-
Also known as bond funds, fixed income funds invest a large portion of investors’ money in bonds issued by corporations and governments. Unlike equity funds that rely on capital appreciation from share price growth, fixed income funds aim to provide investors with a steady source of income.
Also, the return generating potential of fixed income funds is not as high as equity funds. However, fixed income funds are much safer than equity funds. Due to the relatively safe nature of these funds and their ability to provide steady income, investors try to include these funds in their portfolios along with equity funds.
3.MONEY MARKET FUNDS :-
While they may sound similar to fixed income funds, money market funds are a different category altogether. These funds invest only in highly rated, short-term investments such as certificates of deposit, T-bills, short-term bonds and dated securities issued by the government.
Since these funds predominantly invest in government securities, they carry the least risk among all the 4 types of mutual funds. This makes money market funds the right choice for risk-averse investors looking for steady returns on their investments.
4.HYBRID FUNDS :-
Also known as Balanced Funds, Hybrid Funds invest the pooled money in both stock and debt securities. The proportion of investment in both stock and debt securities depends on the fund manager and can be fixed or variable in nature.
Typically, the fund managers of hybrid funds maintain a 60-40 split between stock and debt securities, where 60% of the fund is invested in stocks and the remaining 40% in debt.
THE PLAYERS OF THE MUTUAL FUNDS :-
1.Primary Players:-
- Sponsor: A sponsor is the one who establishes the Mutual Fund. He is the promoter of the Mutual Fund. The sponsor is required to invest at-least 40% of the Net worth of the mutual fund.
- Trustees: Trustees are the ones who hold property of the Mutual Fund, for the benefit of the unit holders. The trustee can be an individual person or a company.
- Asset Managing Company (AMC): AMC is a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013 registered with SEBI. AMC is entrusted with the responsibility of managing the various schemes and operations of the Mutual Fund. It decides how to invest the funds of mutual fund. The AMC is the investment manager of the trust.
- Mutual Fund: It is formed under India Trust Act and registered with SEBI for sale of units of mutual funds to the public which pools the funds of unit holders. Unit holders: The person who holds the units of mutual fund is known as Unit Holder.
Secondary Players (Intermediaries of Securities Market):-
- Custodian: The custodian has the custody of all the shares and various other securities bought by the AMC. The custodian is responsible for the safe keeping of all the securities. It is registered with SEBI.
- Transfer Agents: Registered with SEBI to facilitate issue, redemption and transfer of securities. They maintain updated investment records.
- Depository: Depository holds the units in De-mat form to ensure free flow of mutual fund trade.
ADVANTAGES OF MUTUAL FUNDS
1.Professional Management: The funds of Asset Management Company (AMC) are managed by the experience and high caliber professionals who are backed by the dedicated research team. The research team analyses the performance and prospects of the companies for purpose of investments of funds.
2.Diversified Investment: The AMC diversifies the total funds into different sectors or industry for reducing the risk. In short, diversification of funds reduces the risk of investment.
3.Return Potential: Mutual funds provide higher returns as they invest in a diversified basket of selected securities.
4.Low Cost: If we compare this form of investment with the other forms, the mutual funds are less expensive, because the economies of scale is achieved in brokerage, custodial fee, etc.
5.Transparency: It provides regular information to the investors about the value of their investment.
6.Liquidity: The open ended mutual funds are very liquid and it can be easily encashed by the investors. Even the close ended schemes are tradable in the securities market.
7.Tax Benefits: Many mutual funds are tax exempt under section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
8.Protection to the interest of Investors: Being regulated by the SEBI, mutual funds have to comply with the strict rules and regulations designed to protect the interest of the Investors.
DISADVANTAGES OF MUTUAL FUND
Mutual funds may face the following risks, leading to non-satisfactory performance:—
1. Excessive diversification of portfolio, losing focus on the securities of the key segments.
2. Too much concentration on blue-chip securities which are high priced and which do not offer more than average return.
3. Necessity to effect high turnover through liquidation of portfolio resulting in large payments of brokerage and commission.
4. Poor planning of investment returns.
5. Unresearched forecast on income, profits and Government policies.
6. Fund managers being unaccountable for poor results.
7. Failure to identify clearly the risk of the scheme as distinct from risk of the market.
8. Under performance in comparison to peers.
Note:- The information provided on this blog is for educational and informational purposes only, does not constitute a suggestion to invest, ask your financial advisor or do your own research before investing in any instrument. Because there is risk involved in the market.